AI in banking has moved beyond experimentation. The focus is no longer “Can we build it?” but “Can we run it safely, integrate it into real workflows, and prove value quarter after quarter?” That shift is reshaping how AI and banking teams prioritise investments, design operating models, and manage risk.
This guide breaks down how AI is being used in banking today, where it delivers measurable outcomes, and what it takes to scale AI banking solutions across retail, corporate, and investment banking without compromising governance, security, or customer trust.
Why AI in Banking is moving from pilots to operating model
Banks sit on high volumes of structured and unstructured data, alongside process-heavy operations and strict controls. That mix makes the AI use in the banking industry both attractive and demanding. The winners are not the ones with the flashiest demos, but the ones that connect models to systems, define accountability, and design guardrails that stand up to audit.
What has changed recently is the maturity of tooling and architecture. You can now combine predictive models, generative AI in banking, and workflow automation in a single delivery approach. That opens up end-to-end value, not just isolated productivity gains.
Benefits of AI in Banking that matter to leaders
The benefits of AI in banking consistently show up in four places: better customer service, faster operations, improved decision-making, and stronger risk controls. Banks are using AI for credit scoring and fraud detection to increase efficiency and decision quality, supported by real-time monitoring and pattern recognition that help teams prioritise the right cases faster. These practices can reduce manual reviews and, over time, contribute to decreasing operational burden and financial losses.
The most sustainable gains come when AI removes effort from repetitive work and redirects expert capacity to exceptions and higher-impact decisions. McKinsey’s research also emphasises that banks capture material value when they rewire entire domains, processes, and journeys rather than deploying narrow, isolated use cases, and when they avoid spreading investment across too many disconnected initiatives.
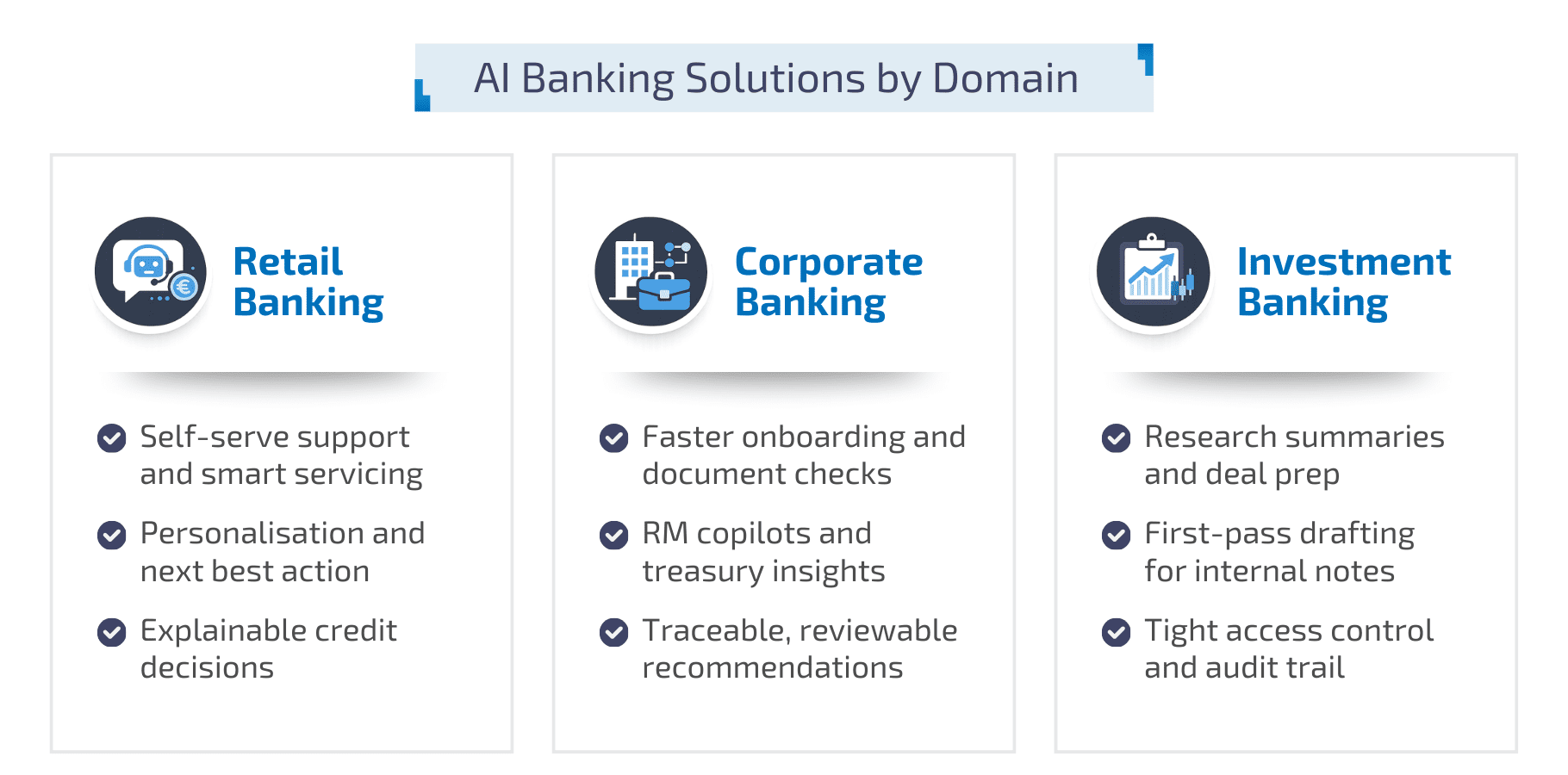
AI banking solutions by domain: retail, corporate, and investment
AI Banking Solutions by Domain
AI in retail banking
AI in retail banking often starts in customer servicing, personalisation, and credit decisions. You see strong impact when AI helps customers self-serve, predicts intent, and supports frontline teams with relevant policy and product knowledge. A well-designed conversational AI in banking can deflect routine queries while keeping handover to a human agent smooth for sensitive cases.
Retail also benefits from smarter collections strategies, churn prediction, and next-best-action recommendations. The key is to ensure that decisions remain explainable and aligned to fairness expectations and internal policy.
AI in corporate banking
AI in corporate banking typically delivers value through relationship manager support and operational acceleration. Examples include onboarding coordination, document checks, and insights for cash management or treasury services. Here, AI banking solutions work best when they connect to internal systems and provide traceable, reviewable recommendations rather than opaque outputs.
Corporate clients also expect consistency. That makes governance and service quality as important as model performance, especially when AI influences client communications and advice workflows.
AI in investment banking
AI in investment banking and capital markets is increasingly shaped by language-heavy work. IOSCO highlights AI’s role in areas such as investment strategies and operational efficiency, and notes that recent advances include the emergence of foundation models and large language models. These capabilities support tasks like summarising research, drafting internal notes, and accelerating first-pass content for deal teams, as long as access controls and oversight are designed in from the start.
The hard part is not content generation. It is ensuring data segmentation, permissioning, and a clear audit trail so that confidential information does not leak across teams or client contexts.
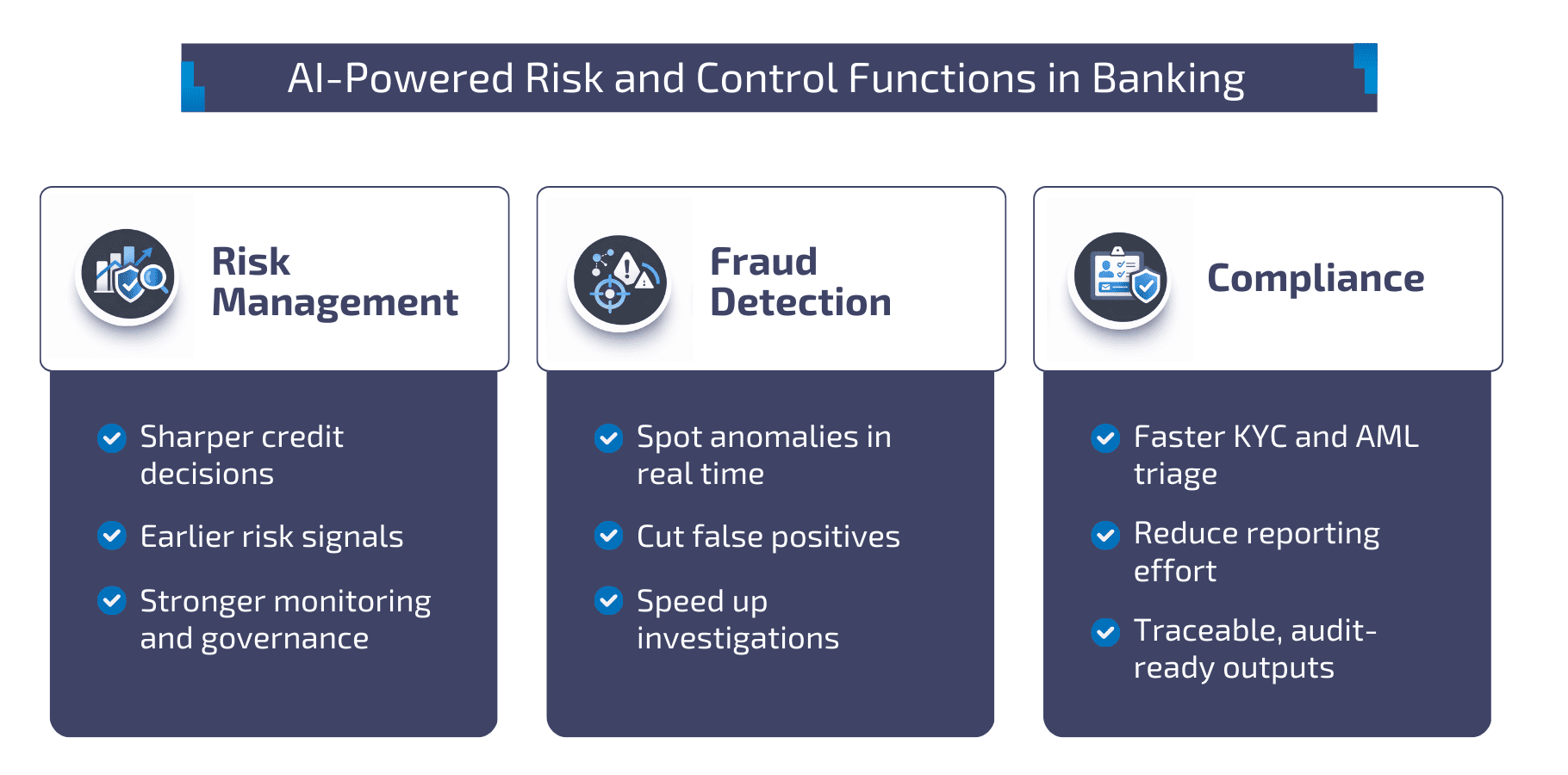
AI-Powered Risk and Control Functions in Banking
AI-Powered Risk and Control Functions in Banking
AI in risk management in banks
AI in risk management in banks is increasingly used to sharpen decision-making in areas such as credit scoring, where banks report higher accuracy through predictive analytics and improved risk assessments.
To scale safely, AI has to be treated as part of the bank’s control environment, with clear governance and ongoing monitoring. Supervisors and standard-setters explicitly warn that AI in banking raises prudential and financial stability challenges, and that model risk, data quality, and governance vulnerabilities require active monitoring and coordination.
Fraud detection using AI in banking
Fraud detection using AI in banking is one of the clearest value cases because outcomes are measurable and feedback loops are strong. AI based fraud detection in banking helps identify anomalies, reduce false positives, and prioritise the right alerts for investigation teams. Over time, this lowers operational load and improves response times.
Regulators’ survey data also shows continued growth in planned AI usage for fraud detection across financial services, reinforcing that fraud-focused AI banking solutions are becoming mainstream rather than experimental.
AI for compliance in banking
AI for compliance in banking can accelerate regulatory compliance and reporting workloads, which many firms expect to expand over the next few years.
In financial crime contexts, FATF highlights that AI introduces developing risks and vulnerabilities through the lens of AML/CFT/CPF, which makes traceability and controls essential.
For EU-regulated firms, the EBA also notes that implementing the AI Act alongside existing banking and payments frameworks will require coordinated supervision and effective integration of overlapping obligations, particularly in high-risk use cases.
Conversational AI in banking and generative AI in banking
Conversational AI in banking is most effective when it is designed around customer journeys, not just FAQs. It can handle routine requests, guide users through forms, and support secure authentication flows, provided that escalation paths are clear and failures are handled safely. The difference between a good and bad deployment is often tone, routing logic, and how well the bot understands what it should not answer.
Generative AI in banking is strongest for knowledge-intensive tasks: summarising policies, drafting communications, and supporting internal teams with fast, grounded answers. Use it to reduce time spent searching and writing, while keeping human review in place for regulated outputs.
Agentic AI in banking: from chat to end-to-end workflows
Agentic AI in banking goes beyond “ask and answer”. It can run end-to-end workflows across systems, with tasks coordinated at different levels of autonomy. Agentic AI is rising in banking and payments, and it delivers the most value when embedded into real customer journeys and operational workflows, not kept as a standalone chat layer.
To deploy it safely, autonomy must be bounded by policy, permissions, and human oversight. Banks also need strong data governance and careful management of third-party dependencies. Governance has to cover build, deployment, and ongoing change, especially where human–AI interaction and outsourcing can introduce new risks. In practice, this means strict access controls, segregation of duties, clear approvals, and continuous monitoring so workflows stay auditable and reliable when they touch customer data or financial outcomes.
AI banking app: what changes in digital channels
An AI banking app can provide smarter in-app support, personalised insights, and proactive nudges that improve financial wellbeing and reduce service demand. Customers benefit from clearer guidance and faster resolution, while teams benefit from fewer calls and better quality of information at the point of interaction.
The main constraint is trust. You need predictable behaviour, secure data handling, and consistent experience across channels. A strong deployment focuses on reliability and guardrails first, then expands capability over time.
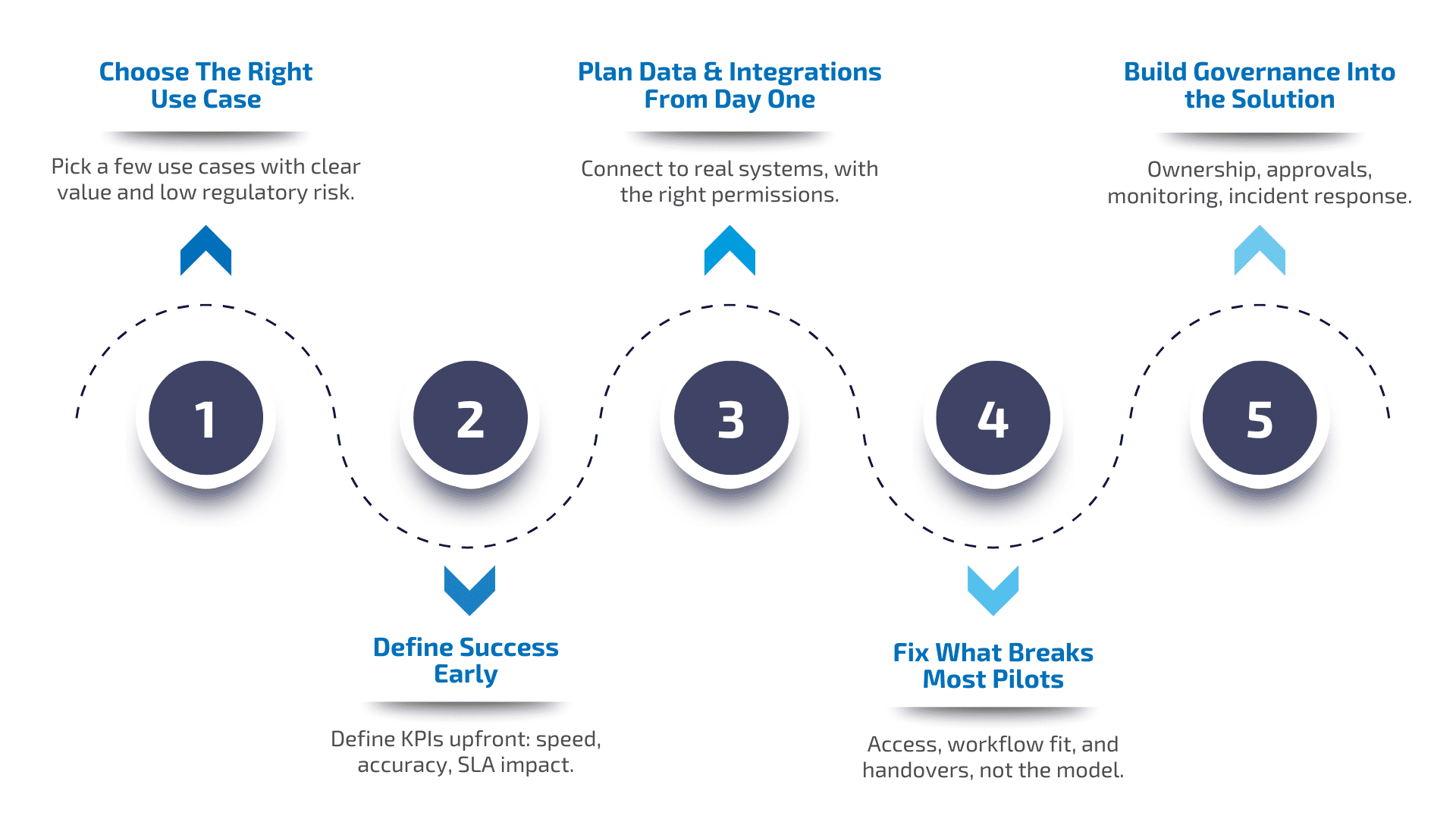
A practical roadmap to scale AI in banking
AI in Banking Framework
- Start with use cases that combine high value and manageable risk.
- Define what “good” looks like using measurable outcomes such as reduction in false positives, time-to-resolution, loss prevented, or improved SLA performance.
- Then design the data and integration layer early.
- Many projects stall not because the model fails, but because systems, access controls, and workflow fit were not addressed.
- Finally, treat governance as a product, not paperwork. Define ownership, approval paths, monitoring, and incident response.
If you can operate the solution under real constraints, scaling becomes repeatable across teams and countries.
How BGTS helps you deliver AI banking solutions you can run
To move AI in banking from pilot to sustained business outcomes, you need solutions that are designed for secure operations, seamless integration, and audit-ready governance. BGTS supports banks with end-to-end capability from AI strategy and readiness through engineering, integration, and optimisation, ensuring AI delivers measurable impact across retail, corporate, and investment banking.
If you would like to prioritise the right use cases and define a practical delivery roadmap, explore BGTS AI services, or Get in touch to discuss your priority use cases, operating model, and a practical delivery roadmap.
FAQs
How is AI being used in banking today?
How AI is used in banking depends on the domain, but patterns are consistent: customer service automation, fraud and transaction monitoring, risk decision support, compliance triage, and internal copilots for frontline productivity. The most effective programmes tie these capabilities to a few priority workflows with clear KPIs.
Will AI take over banking jobs?
Will AI take over banking jobs is the wrong framing. Roles will change. Repetitive tasks shrink, while oversight, exception handling, and decision quality become more important. Professionals should expect role redesign, new governance responsibilities, and demand for skills in data stewardship, model risk, and workflow design.







